OpenBNG on SONiC: Evolve from Legacy BNG to High-Performance, Disaggregated OpenBNG
written by Asterfuison
Table of Contents
Introduction
With the explosive growth of 5G, high-definition video, and online gaming, networks require higher performance and greater flexibility. Traditional edge routers are increasingly unable to meet the demands of modern broadband access networks. This article starts with BNG networks to explain the concepts, architecture, and practical considerations of OpenBNG on SONiC, while referencing our company’s product line.
Ⅰ. What is BNG Network
BNG (Broadband Network Gateway) is the core device in broadband access networks, responsible for user access management, policy control, and data forwarding. Compared to traditional edge routers, a BNG not only provides routing functions but also manages user sessions, policies, and billing. In simple terms, a BNG acts as a bridge between household broadband users and the internet or service providers. This bridge serves both the operator side (for billing and policy management) and the user side (for IP address assignment and session management).
1. Network Architecture

From an architectural perspective, BNG is positioned between the access/aggregation layer and the core network. User CPEs (GPON AP or XGS-PON AP) connect through the ODN via a GPON or XGS-PON OLT and then pass through aggregation switches before reaching the BNG.
Unlike traditional edge routers, BNGs manage not only packet forwarding but also user authentication, policy enforcement, and billing, ensuring both efficiency and manageability.
Roles of each network layer:
- Home Network: User-side residential or office network.
- Access: Aggregates user traffic from GPON/XGS-PON networks.
- Aggregation: Consolidates traffic from the access layer into regional aggregation points.
- Broadband Edge: Layer where the BNG resides, handling sessions and policies.
- Core: Core network carrying network-wide data flows and inter-region routing.
2. Core Functions
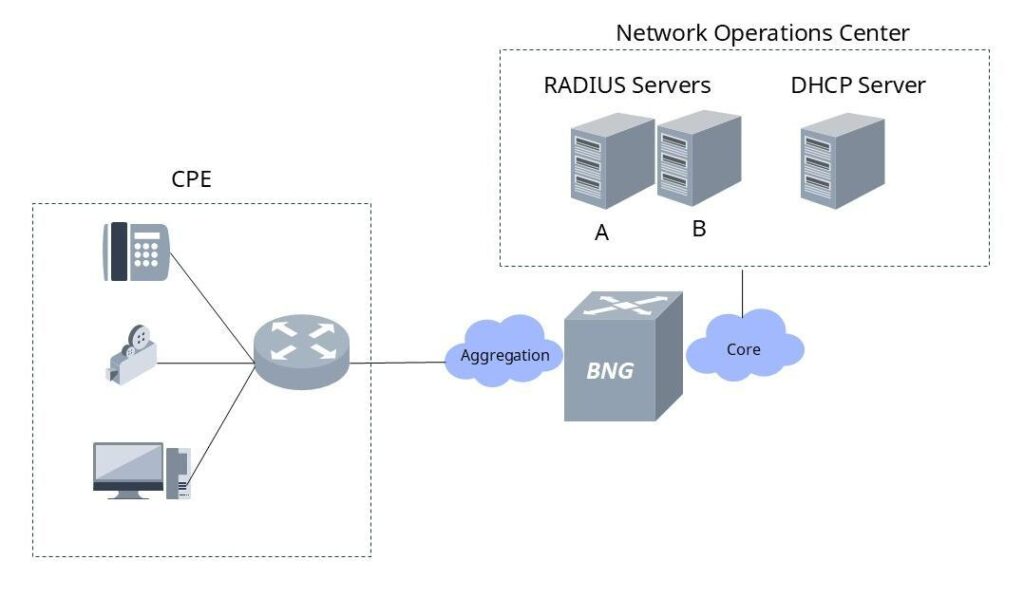
The main functions of a BNG include:
- CPE Connectivity: Manages access and authentication for user devices (CPEs). CPEs connect through the access network to the BNG, where sessions and authentication are managed.
- IPoE / PPPoE Session Establishment: Supports two session models:
- PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet): Session control via point-to-point protocol.
- IPoE (IP over Ethernet): IP address assignment via DHCP.
- AAA / RADIUS: Interaction with RADIUS servers for user authentication, authorization, and billing.
- DHCP Services: Dynamic IP address allocation to downstream devices through DHCP servers.
- Routing Advertisement: Distribution of routing information to users for flexible traffic forwarding.
- The aggregation layer employs a suite of key technologies, namely traffic classification, VLAN management, multicast traffic handling, QoS assurance, and security protection.
Ⅱ. OpenBNG on SONiC Evolution and Industry Trends
With network virtualization and the development of open ecosystems, traditional BNGs are evolving toward OpenBNG. This evolution is driven by high costs, hardware-software coupling, and vendor lock-in of traditional BNGs.
To address these issues, TIP(Telecom Infra Project), through its OpenBNG project, actively develops and promotes open-source solutions that follow the OpenBNG concept and comply with Broadband Forum standards, thereby accelerating the adoption and deployment of OpenBNG in the industry.
As the article title suggests, OBNG is disaggregated, which is reflected in three aspects:
- Hardware-Software Disaggregating: BNG software can run on any white-box device or standard hardware, independent of vendor-specific platforms.
- Architectural Disaggregating(CUPS): At the architectural level, Nokia led the definition and implementation of the DBNG CUPS (Control and User Plane Separation) standard. The Broadband Forum clearly defines, through TR‑459, the architecture, interfaces, and behaviors for implementing control and user plane separation in broadband access networks. In this architecture, the Control Plane manages policies and user sessions, while the User Plane handles actual traffic forwarding. They can be deployed on separate hardware platforms, synchronizing control information and session state via PFCP (Packet Forwarding Control Protocol). The system can scale flexibly according to traffic demands. This separation enables operators to maintain high network performance while allowing independent upgrades and flexible expansion for different service scenarios.
- Functional Disaggregating: BNG functions are modular and can be deployed as needed. Modules such as PPPoE, IP routing, and VPN can be independently selected and combined for lightweight, efficient deployment.
These three levels of disaggregating provide OpenBNG with high flexibility. In particular, separating the control and user planes (DBNG) allows deployment on different hardware and dynamic scaling based on traffic, meeting performance and expansion requirements in various scenarios.
Ⅲ. Software Package and Hardware of OpenBNG on SONiC
In the OpenBNG architecture, software and hardware are highly disaggregated. Software functions are delivered through different packages, while hardware platforms can be chosen flexibly.
Software Overview
To implement full OpenBNG functionality, systems must follow Broadband Forum broadband access standards, including TR‑059, TR‑101, and TR‑146. These standards ensure compatibility across hardware and standardized operation for control and user planes.
The OpenBNG software is divided into packages, each defining a specific set of functionalities:
| OpenBNG Package | Features |
| BNG Software Package (BSW) | PPPoE, IPoE, VPN, IPv4/6 routing, AAA (RADIUS), QoS, Multicast |
| Router Software Package (RSW) | IP/MPLS routing, Link Aggregation, BFD |
| Provider Edge Software Package (PESW) | L2VPN, L3VPN, E-VPN |
| OpenBNG Management & Security | TWAMP, NETCONF, gRPC, Telemetry, IPsec, TACACS+ |
These packages together provide the full OpenBNG feature set, including session management, policy control, and user traffic forwarding.
Flexible Hardware Deployment
OpenBNG software is hardware-agnostic and can run on multiple platforms, including:
- DPU / white-box devices: e.g., Marvell OCTEON 10 series for control or user plane processing.
- Programmable switching ASICs: e.g., Intel Tofino for accelerating user plane forwarding.
This separation allows operators to deploy control and user planes according to traffic demands, enabling flexible scaling and cost optimization.
Ⅳ. Asterfusion Hardware Platforms for OpenBNG on SONiC
The performance and scalability of OpenBNG depend on the underlying hardware. Different platforms can support different functions. Combined with OpenBNG software, they allow flexible deployment for various scenarios. Typical choices in our product line include:
- ET2500 Series: Based on Marvell OCTEON10 CN102, running Ubuntu or Debian. Suitable for control plane deployment and small-scale user plane traffic. Ideal for medium and small networks.
- ET3000 Series: Based on CN103 DPU platform with two DPUs. Supports control plane and high-speed user plane processing. Suitable for large-scale, high-performance deployments.
- X-T Series: Based on Intel Tofino, optimized for user plane traffic forwarding, packet processing, and QoS enforcement.

These hardware platforms combined with OpenBNG software allow operators to deploy control and user planes according to traffic requirements, ensuring high performance and scalable flexibility.
Ⅵ. Conclusion and Outlook
OpenBNG provides a flexible, scalable, and hardware-software disaggregated deployment model for modern broadband access networks. Through CUPS architecture, modular software packages, and adaptable hardware platforms, operators can independently scale the control and user planes, achieving high performance, low latency, and reliable billing.
It is worth noting that, although OpenBNG is developing rapidly, traditional BNG networks still dominate the market. According to the Fundamental Business Insights report, traditional BNG holds a 58.8% market share. Therefore, the ET2500/ET3600 equipped with AsterNOS-VPP is a suitable choice for operators still using traditional BNG. It provides BRAS functionality, including PPPoE, RADIUS, QoS, and NAT, and also supports unified management through a OpenWiFi Controller, ZTP (Zero-Touch Provisioning), and RESTful APIs.
These features make the ET2500 a transitional solution from traditional BNG toward OpenBNG, balancing current broadband access requirements with future network scalability.
Looking forward, with the growth of 5G, high-definition video, and cloud gaming, OpenBNG’s flexibility and openness will be key to broadband network upgrades and innovation. Combined with Asterfusion’s product line, operators can rapidly build future-ready broadband access solutions.
Note: To tell the difference between BNG and BRAS, please refer to BNG Router vs. BRAS Router
Contact US !
- To receive timely and relevant information from Asterfusion, sign up at AsterNOS Community Portal
- To submit a case, visit Support Portal.
- To find user manuals for a specific command or scenario, access AsterNOS Documentation
- To find a product or product family, visit Asterfusion-cloudswit.ch .
- To contact Sales, Send E-Mail to bd@cloudswit.ch





