Enterprise Sonic OS – AsterNOS-V5.2R014 2025 Q3 Major Update, Campus Ready
written by Asterfuison
Table of Contents
Introduction: Milestone for 2025 Q3
As open networks continue to redefine enterprise agility and cost efficiency, enterprise SONiC OS has evolved from community SONiC and is now adopted by major vendors such as Dell and Asterfusion. Asterfusion officially released a major update to our enterprise SONiC OS, AsterNOS-V5.2R014, in Q3.

This release focuses on four key pillars, aiming to deliver outstanding network performance and operational stability for enterprises.
Pillar 1: Core Protocol Stack and Multicast Enhancements for Large-Scale Real-Time Data
The latest Enterprise Sonic OS release, AsterNOS-V5.2R014, introduces critical enhancements to the IP protocol stack, enabling better support for large-scale real-time data transmission in media, campus, and industrial networks built on ethernet switch sonic network os architecture.
New Features:
PIM Support: Fully supports Protocol Independent Multicast (PIMv4) routing. This allows AsterNOS to efficiently handle point-to-multipoint traffic in environments, such as large-scale video distribution, remote education, or real-time data streaming.
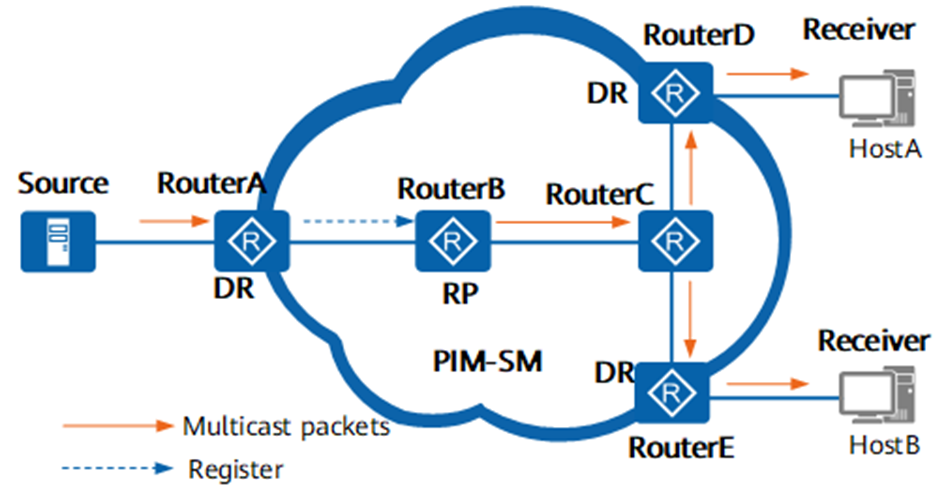
Supported Capabilities:
- PIM-SM Mode: This release focuses on Sparse Mode (SM), establishing efficient shared trees and source trees within multicast domains for data forwarding, avoiding the traffic flooding issues seen in PIM-DM.
- Dynamic Multicast Source Registration & Group Membership: Sources and receivers can dynamically register and join multicast groups via control messages.
- Dynamic Multicast Forwarding Tree Generation: The device automatically constructs optimal forwarding trees based on multicast packets and membership information.
- Static Configuration Compatibility: To accommodate complex enterprise environments, administrators can manually configure multicast entries to define fixed forwarding paths.
Pillar 2: Security and Compliance – From Link Encryption to Management Auditing
Enterprise Sonic OS AsterNOS-V5.2R014 enhances data transmission security and operational compliance, providing protection from hardware to software layers.
New Features:
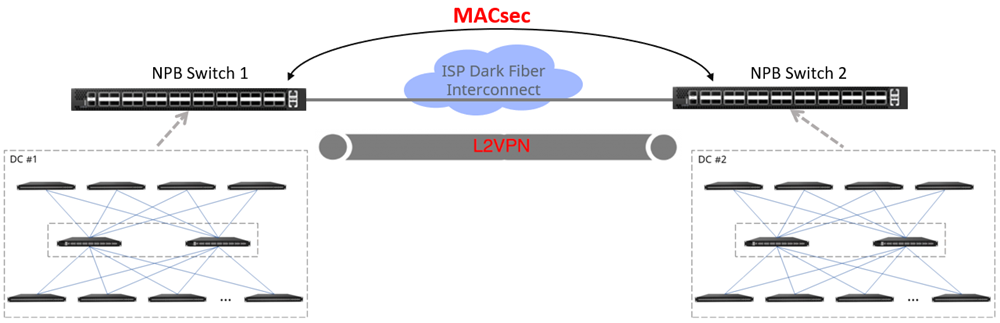
- MACsec (IEEE 802.1AE): Offers link-level, hop-by-hop encryption to ensure that data, especially over public or shared networks, is protected from eavesdropping and tampering.
In practical deployments, this technology has been applied to dark fiber connections between data centers, significantly enhancing data security.
- RADIUS Authentication Support: Enables management user authentication and authorization through standard RADIUS protocol, meeting enterprise-grade security auditing and fine-grained access control requirements.
Enhancement:
PTP Time Synchronization over MACsec: The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) has been optimized to operate accurately over MACsec-encrypted links, ensuring precise synchronization for latency- and accuracy-sensitive applications, such as high-frequency trading and 4K/8K video streaming.
Pillar 3: Fabric Resilience and High Availability for Service Continuity
AsterNOS-V5.2R014 introduces resilience and redundancy mechanisms for VXLAN networks, ensuring rapid recovery or seamless migration in the event of any single-point failure.
New Features:
- EVPN Multihoming Support: Full support for EVPN Multihoming. It allows access-layer devices to connect to two or more Leaf nodes simultaneously, significantly improving redundancy and availability at the VXLAN access layer.
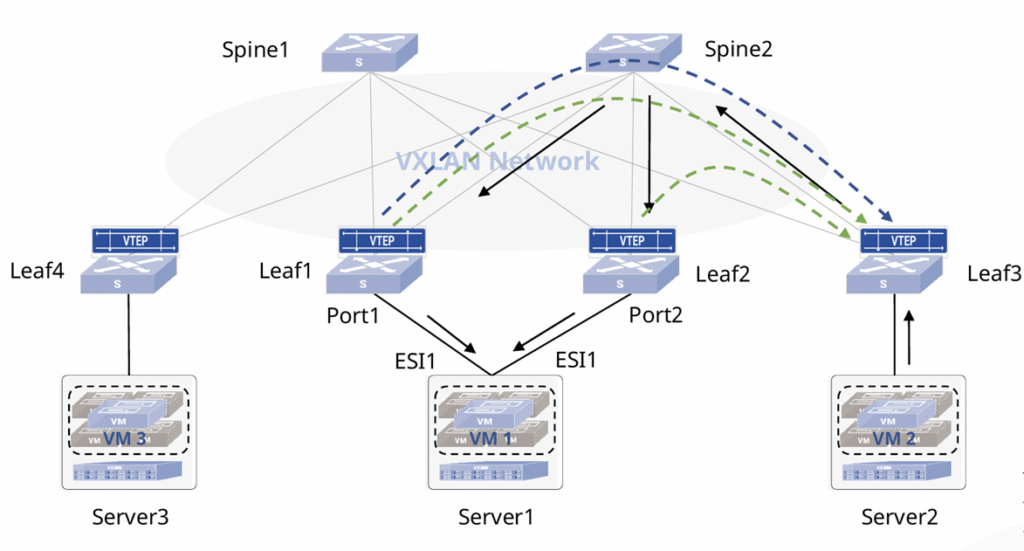
As shown in figure 3, Leaf1 and Leaf2 under the same ESI 1 both serve as uplinks for Server1. When Server2 accesses Server1, there are two possible paths:
Leaf3 → Spine2 → Leaf1 → Server1Leaf3 → Spine2 → Leaf2 → Server1
This setup enables load balancing, while the DF election and Split Horizon mechanisms ensure that BUM traffic remains unique across multihomed environments, preventing loops.
Note: ESI (Ethernet Segment Identifier) uniquely identifies each Ethernet segment and denotes all associated PE (Leaf/VTEP) devices.
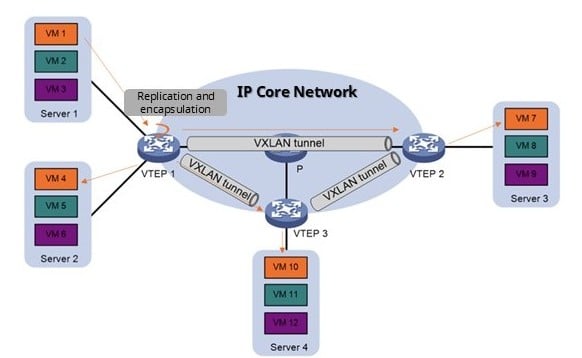
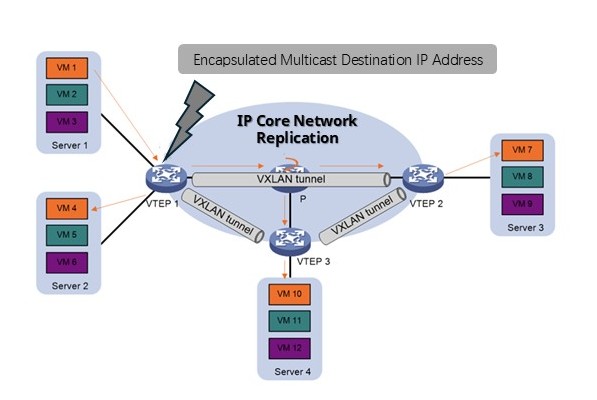
- VXLAN Multicast Mode: In VXLAN networks, BUM (Broadcast, Unknown Unicast, Multicast) traffic can be handled in two ways:
- Ingress Replication (Figure 4): The source VTEP replicates BUM traffic and sends copies to each destination VTEP.
- Multicast Mode (Figure 5): The VXLAN packet is encapsulated with a multicast destination address, allowing the underlay network to replicate the traffic. This reduces the uplink load on the source VTEP and improves overall network efficiency.
- Link Flapping Detection: Introduces alerts and handling mechanisms for link flapping, helping network operators quickly identify and resolve unstable physical link issues.
Pillar 4: Intelligent Operations and Edge Optimization for Reduced OPEX
This release of Enterprise Sonic OS focuses on intelligent PoE and simplified edge operations to minimize manual intervention and enhance reliability.
New Features:
- Intelligent PoE Management: Introduces PoE PD Alive Check, which automatically monitors the status of powered devices (PDs). In case of anomalies, the system can trigger alerts or perform automatic reboot operations, reducing manual intervention at the edge and improving service continuity.
Optimizations:
- Legacy Detect Enabled by Default: Ensures broader compatibility with legacy devices that do not support standard PoE (e.g., IEEE 802.3af/at/bt).
- Simplified Default Configuration: For CX102S switches, redundant default VLAN configurations have been removed to eliminate potential risks associated with default settings.
Conclusion: Asterfusion is Ready !
The release of AsterNOS-V5.2R014 Q3 Major Update marks a new level of maturity for Enterprise SONiC OS in security compliance, fabric resilience, and operational efficiency.
Ready to break free from vendor lock-in and embrace a more secure, open, and intelligent network future?
Take action now:
📅 Upgrade Experience: Try the latest AsterNOS-V5.2R014 image today.
📥 View Full Release Notes



