How Asterfusion Designs a 256K-GPU Ultra-Ethernet AI Training Network
written by Asterfuison
In the era of large language models (LLMs) and generative AI, the center of gravity in the computing arms race is shifting. Raw GPU performance alone is no longer the decisive factor. Instead, the real differentiator lies in how effectively tens of thousands of GPUs can work together as one system. When massive GPU clusters must coordinate trillions of parameter updates through continuous synchronization, the network is no longer just a transport layer. It becomes the lifeline of AI training performance.
In this article, we take a deep dive into how Asterfusion builds a hyperscale, ultra-low-latency, congestion-free AI training network—one that not only rivals but, in key scenarios, surpasses traditional InfiniBand fabrics.
1. What Is an AI Training Network?
At its core, an AI training network is the nervous system that interconnects thousands—or even hundreds of thousands—of GPUs (or NPUs and other accelerators) into a single distributed computing engine.
In today’s LLM era, no single GPU has enough memory or compute capacity to train models like LLaMA 3 or GPT-4, which contain tens or even hundreds of billions of parameters. Training must therefore be distributed across massive GPU clusters.
To function as a coherent system, these GPUs must exchange data frequently, deterministically, and at extremely high speed. The backend network that carries this compute communication is what we call the AI training network.
1.1 How Is It Different from a Traditional Data Center Network?
If a conventional data center network is like a city’s road system—handling web requests, file transfers, and transactional traffic—then an AI training network is more like an F1 racetrack or a high-pressure oil pipeline.
- Traffic patterns are fundamentally different
Traditional networks handle asynchronous, bursty, and mostly independent flows. AI training traffic is highly synchronized and periodic. After each computation phase, tens of thousands of GPUs simultaneously emit massive gradient data bursts. - Loss tolerance is radically lower
In a typical enterprise network, packet loss may result in slightly slower page loads. In an AI training network, a single dropped packet can stall tens of thousands of GPUs, causing seconds of idle time and dramatically reducing the utilization of extremely expensive compute resources.
1.2 The Role of the Network in Distributed Training
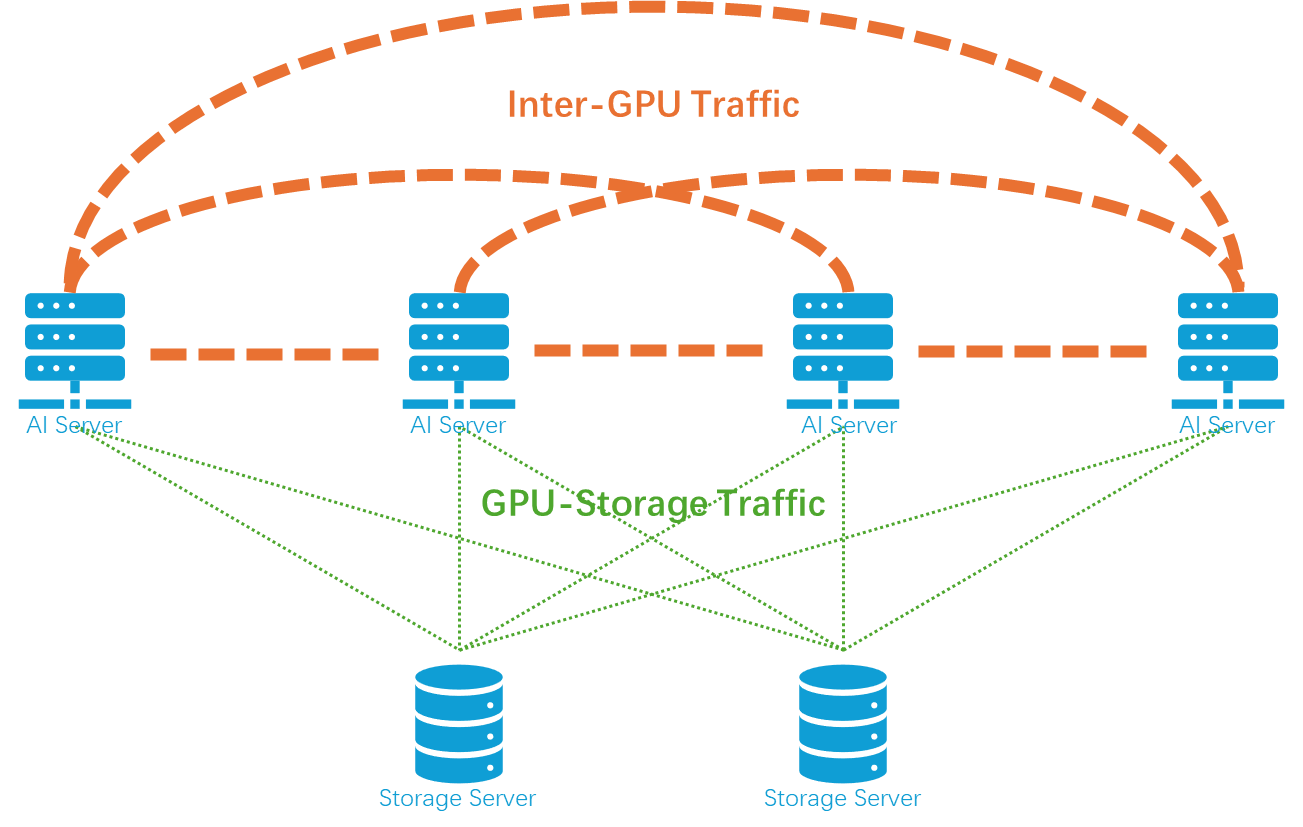
At the heart of distributed AI training lies collective communication, including operations such as:
- All-Reduce: GPUs aggregate local results, compute a global average, and redistribute it to all nodes.
- All-Gather: Each GPU contributes partial data, and every GPU receives the complete dataset.
- For more: Unveiling AI Data Center Network Traffic
The efficiency of these operations directly determines synchronization speed. If the network introduces latency or congestion, GPUs finish computation and then sit idle, waiting for data.
This is why the industry focuses so heavily on JCT (Job Completion Time): a faster network translates directly into faster model convergence.
1.3 The Two Dominant Technology Paths Today
AI training networks are currently built on two major paradigms:
- InfiniBand (IB)
A mature, proprietary fabric known for excellent performance and native losslessness—but also high cost and a closed ecosystem. - High-Performance Ethernet (RoCEv2)
Enabled by vendors like Asterfusion, modern Ethernet fabrics running RoCEv2, combined with adaptive routing and ultra-low-latency switch architectures, can now match or exceed InfiniBand performance, while remaining open, flexible, and cost-efficient.
In short: an AI training network exists to allow tens of thousands of GPUs to think and learn as one brain—with ultra-low latency, zero loss, and deterministic performance.
2. What Defines a Great AI Training Network?
From Asterfusion’s perspective, evaluating an AI training network goes far beyond port speed. The true benchmarks are:
- Ultra-Low Latency
Distributed training efficiency is dictated by the slowest path. Lower latency reduces GPU wait time during synchronization and shortens overall training cycles. - Lossless, Congestion-Free Operation
RoCEv2 is highly sensitive to packet loss. In large-scale concurrent communication, congestion-induced retransmissions can severely inflate JCT. - High Network Utilization
AI training produces sustained “elephant flows.” If network utilization is low, expensive GPUs are effectively being wasted. - Massive Scalability
As model sizes approach trillion-parameter scale, the network must scale horizontally to 100K GPUs and beyond without performance collapse. - Efficient Support for Collective Communication
Native optimization for All-Reduce, All-Gather, and All-to-All patterns—with intelligent scheduling and load balancing—is essential.
3. Asterfusion’s AI Training Network Topology: A 256K-GPU Blueprint
To support a 256,000-GPU training cluster, Asterfusion designed a physical fabric inspired by Ultra Ethernet principles.
Two-Tier Clos Architecture with an 8-Rail Design
Asterfusion employs a two-tier Spine-Leaf topology combined with an industry-leading 8-Rail architecture. At full scale—256K GPUs, each provisioned with 400G bandwidth—the fabric consists of:
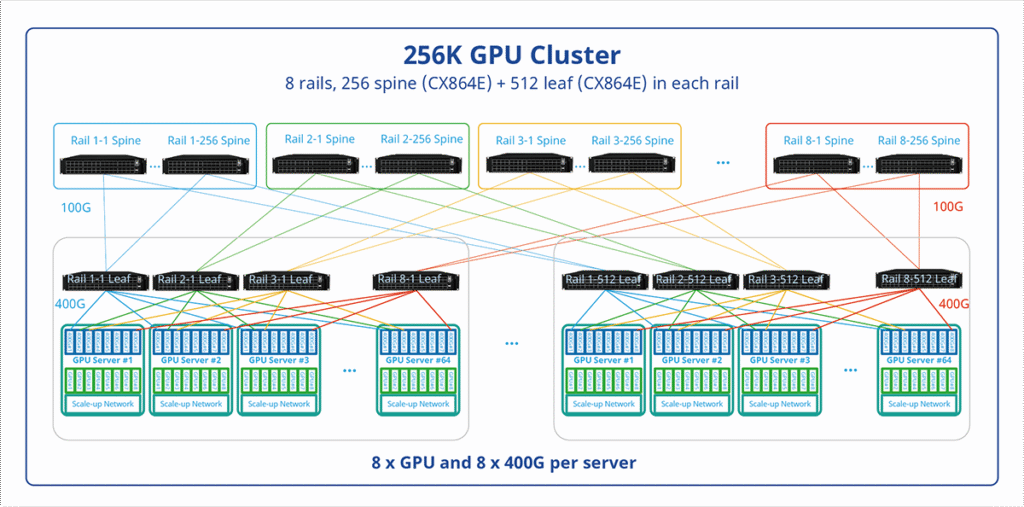
- 256 Spine switches
- 512 Leaf switches
The 8-Rail design distributes GPU-to-GPU traffic across multiple independent physical planes, dramatically increasing path diversity and reducing the risk of incast congestion.
By minimizing hop count and leveraging ultra-high-radix switches, Asterfusion achieves global-scale compute interconnection with a surprisingly compact number of devices.
4. Why Asterfusion Ultra Ethernet Can Surpass InfiniBand
Asterfusion’s advantage is built on four core technical pillars.
Pillar 1: 560-Nanosecond Latency (CX864E-N)
The flagship CX864E-N 800G switch delivers an end-to-end latency as low as 560 nanoseconds—a level once thought exclusive to InfiniBand.
This eliminates the traditional physical-layer performance gap and unlocks the full communication potential of modern GPUs.
Pillar 2: Four-Layer Congestion-Elimination Strategy
Traditional ECMP hashing often leads to link contention. Asterfusion raises network utilization from ~60% to 97% using a four-pronged approach:
- INT-Driven Adaptive Routing: Real-time telemetry detects queue pressure and dynamically avoids congestion.
- Packet Spray: Traffic is distributed at packet granularity instead of flow granularity.
- Flowlet-Based Load Balancing: Natural traffic gaps trigger rebalancing without reordering.
- WCMP: Weighted path optimization for asymmetric topologies.
Pillar 3: INT-Driven, Topology-Aware Collective Communication Optimization
Instead of treating AI traffic as generic packets, Asterfusion leverages in-band network telemetry (INT) to enable topology-aware optimization for AI collective communication. by continuously observing real-time congestion, queue depth, and path utilization inside the fabric, the network dynamically aligns communication behavior with the physical topology. This allows efficient support for a wide range of distributed training patterns, including:
- Ring-based, Tree-based, and Halving–Doubling communication models
- Pipelined implementations of All-Reduce, All-Gather, and All-to-All


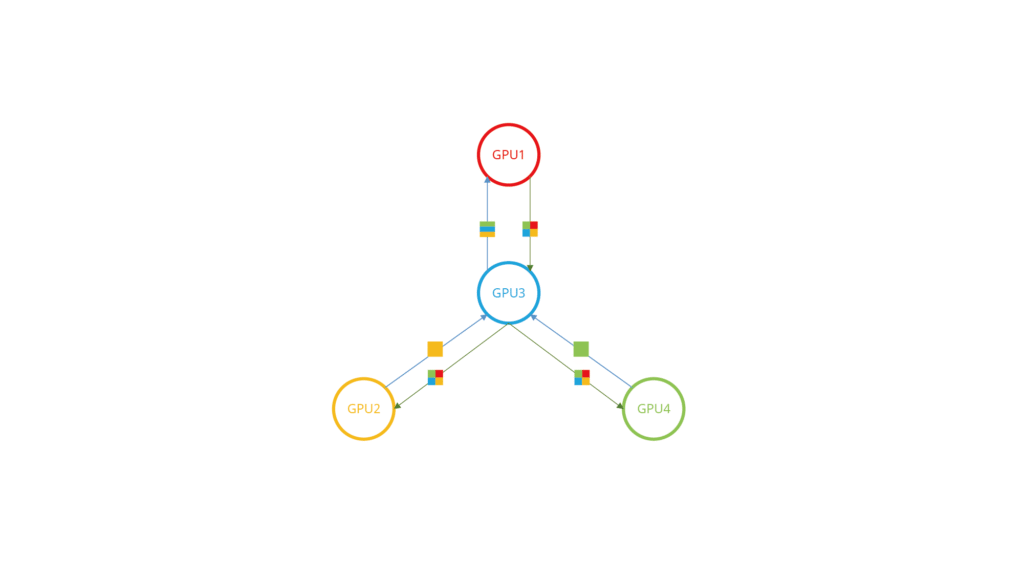

With INT-driven visibility, traffic scheduling and path selection are optimized at runtime to minimize synchronization stalls and avoid hotspots. As a result, GPUs spend less time waiting for data, and the network sustains higher effective throughput under heavy collective workloads.
This topology-aware approach significantly improves both GPU utilization and network utilization, especially in large-scale, multi-hop training fabrics where traditional static routing often becomes the bottleneck.
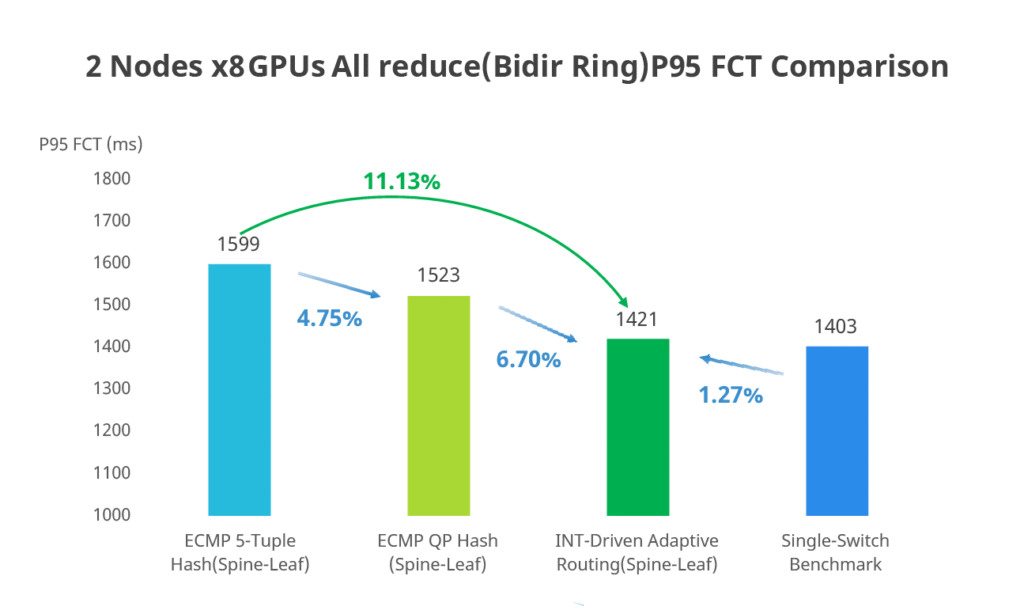
Pillar 4: Dramatically Reduced Tail Latency
Compared to conventional RoCE or IB switches, Asterfusion reduces P95 end-to-end tail latency by 11%.
In AI training, that 11% directly translates into fewer synchronization stalls and faster iteration cycles.
5. Performance Validation: Beating InfiniBand in Practice
Performance claims must be backed by data. In Asterfusion’s lab, extensive benchmarks were conducted.
LLaMA-2 Training (16 GPUs)
- Single-switch topology: Asterfusion RoCE and Mellanox IB show comparable step time.
- Two-switch back-to-back topology: Asterfusion achieves 3.38% lower per-step training time, highlighting superior congestion control in multi-hop scenarios.
LLaMA-3-39B Simulation (400G Testbed)
Using IXIA AresONE-S 400G traffic generators:
- JCT improvement: ~6.12% reduction, driven by INT-based adaptive routing.
- Overall gain: Across realistic AI workloads, Asterfusion delivers 3–5% faster JCT than IB fabrics.
Conclusion: Choosing Asterfusion Is Choosing the Future of AI
From 100G to 800G and beyond, Asterfusion proves that open Ethernet can match—and exceed—proprietary fabrics in performance, while delivering superior flexibility, scalability, and TCO.
If you are building the next generation of 10K-GPU or 100K-GPU AI training clusters, Asterfusion provides a congestion-free, ultra-low-latency, AI-native Ethernet foundation.
Learn more about Asterfusion AI Training Network
👉 https://cloudswit.ch/solution/ai-training-network/
Recommended Hardware
- CX864E-N – 51.2T 800G powerhouse for Spine layers
- CX732P-N – High-density 400G Leaf switch optimized for GPU clusters
Build faster. Train smarter. Scale further.
With Asterfusion, your AI network is finally ready for the models of tomorrow.





