Table of Contents
In the 5G era, our network infrastructure faces new challenges: massive endpoints, ultra-high bandwidth and extreme low latency. For nowadays, network latency (delay) is no longer a strange term to most people, we often hear the word “network latency,” so what is network latency? What causes the network delay? How do you test your network ‘s latency and how to ultimately resolve it? This article will explore the above questions.
What is Network Latency?
In networking terms, network latency = network delay
Network latency is a design and performance characteristic of telecommunication networks. It specifies the delay at which some data is transferred from one communication endpoint to another over the network. It is usually measured in multiples or fractions of seconds. Therefore, the lower the latency of the network, the faster the speed. So, if you need a high-speed connection, make sure your network has the lowest latency possible.
What causes network delay?
There are many reasons for network delay, which may include the following factors:
- Propagation delay-The time when a signal travels through the media -It needs time to transfer a packet from source to destination whatever fiber optics or cables. Noted that, longer distance means longer delay, where requests are made comes from the server that responds to those requests.
- Processing delay-The time for the router and switches processes the data header. Each gateway takes time to check and change the header of the packet, so it spends a lot of time for Ethernet packets to pass through the Ethernet switch.
- Queuing delay-The time a packet takes in the routing queue. A congested network carrying too much data requires content to be queued and delivered sequentially. So, packet has to wait for its turn.
- Security processing delay: Anti-virus and similar security procedures usually need time to perform message reassembly and dismantling before sending.
- Storage delay: Packets, sometimes, are suffered from storage or disk access delays on intermediate devices such as switches and bridges.
- User’s perspective delay, users’ software malfunctions can cause some delays.
How to test your network latency?
Measuring network latency in packet-switched networks include
- One-way delay time (The time from the source sending the packet to the destination receiving it)
- Round trip delay time (The time from source to destination + destination back to source ‘s round trip delay).
Since round -trip delay can measure from a single point, it’s more often used.
Switch delay measured tools include
Switch delay measured from port to port on an Ethernet switch. It can be showed in several ways, relaying on the switching paradigm adopted by the switch. It can be measured by different methods such as, IEEE specification RFC2544, Ping Pong or Netperf.
- IEEE specification RFC2544 offers an industry-accepted standard to measure store and forward devices’ delay.
- Ping Pong is a way to measure latency in a high-performance computing cluster, by measuring round-trip times for remote procedure calls (RPCS) sent over a messaging passing interface (MPI).
- Netperf could measure delay with request or response tests (TCP_RR and UDP_RR).
With this analysis, network administrators can reroute packets to minimize network latency.
Difference of Network Latency, Throughput and Bandwidth
Latency, throughput and bandwidth are three important contributors to network transmission’s quality. Although these three factors work together, they measure different things. For easier understand it, we could imagine that data packets flow as high-traffic road.
- Bandwidth is the width of the road. The narrower the road, the fewer cars are allowed to pass through it. (The less data is sent back and forth.) The wider the road (the communication band), the more data can flow over it simultaneously. Essentially, bandwidth is the maximum number of packets that can travel across the network at any given time.
- Latency is the time it spends for a car (data) to travel from one point (client) to destination(server) on a network. Latency is a measurement of time instead of downloading how much data over time.
- Throughput is the total number of cars that can pass through the road (the volume of data transmitted) during a specified period. Throughput is actually the average amount of packet that can passes through in a given time. Noted that throughput does not necessarily equate to bandwidth, as it is influenced by latency and other factors.
Low latency and low bandwidth mean there will be low throughput. This means that while packets should technically be delivered without delay, but low bandwidth indicates that there can still be severe congestion. However, with high bandwidth and low latency, throughput is greater, and connections are more efficient
How to Build an Ultra-low Latency Data Center Network
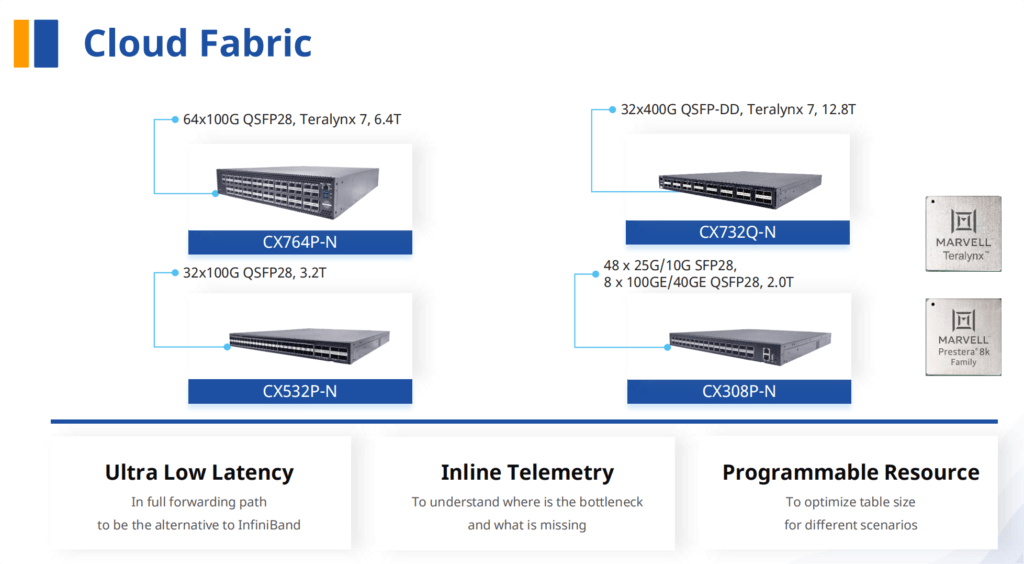
To cope with the rapid development of cloud network and reduce network latency with Ethernet switches in data center scenario, Asterfusion offers industry-leading low latency switches.
Asterfusion CX-N Low Latency Switch
Enables low latency networks no longer the preserve of the financial industry
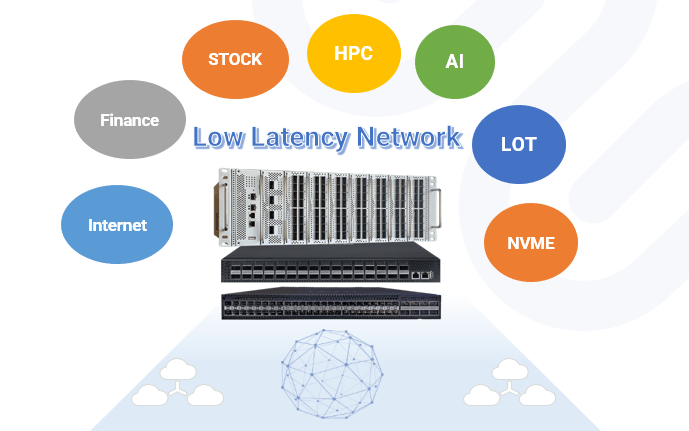
CX-N series’ offers ultra- low latency switching capabilities as low as ~500ns in most application scenarios. Allowing it to more than satisfy the requirements of latency-sensitive applications, such as NVME, IoT,VR/AR/MR,high-frequency trading, big data analysis, machine learning and etc.,
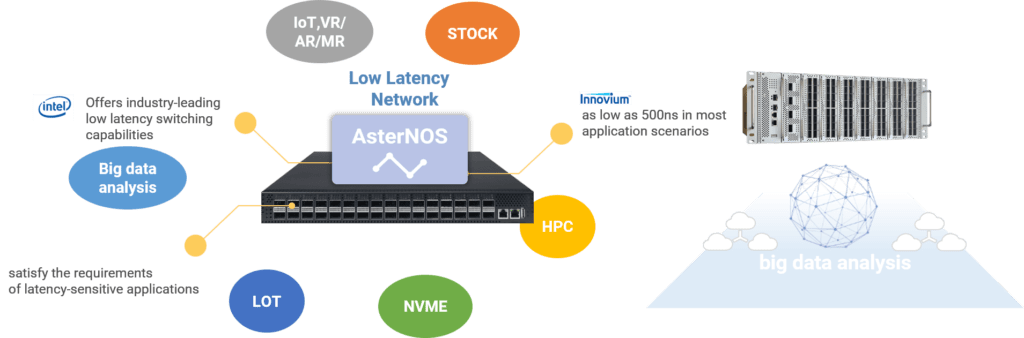
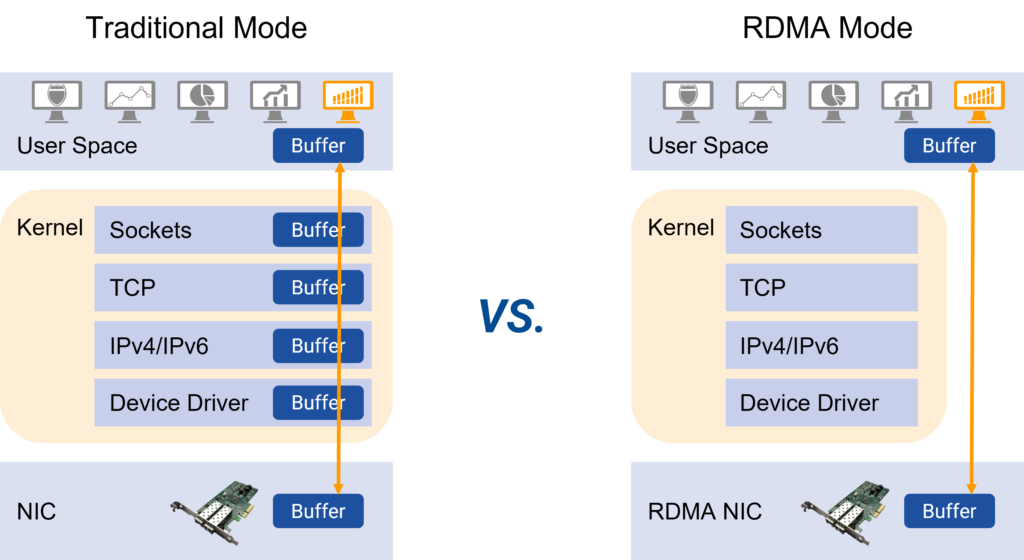
Powerful QoS features for RoCEv2/RDMA, building no congestion low latency network
The CX-N switches supports RoCEv2 which allows remote direct memory access (RDMA) over an Ethernet network. It solves the delay of server-side data processing and frees up the CPU to do more important tasks, such as running applications and processing large amounts of data. It increases bandwidth and reduces latency, jitter, and CPU consumption, helping to build highly efficient and cost-effective data center networks.
PFC creates an independent priority queue for RoCE flows
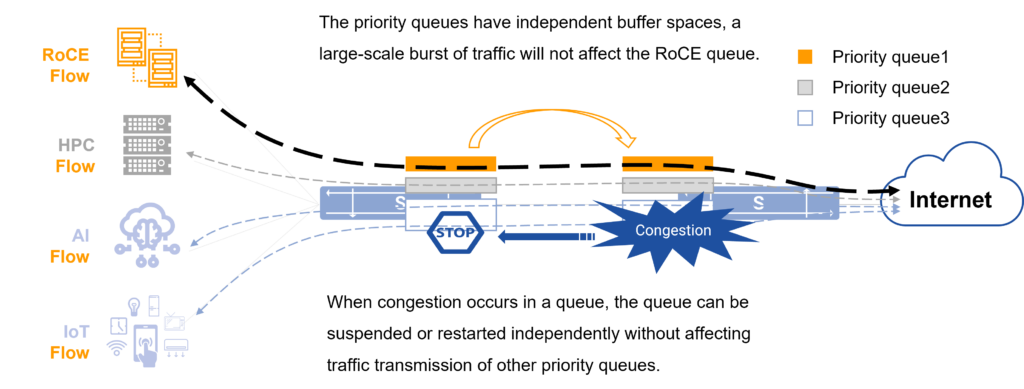
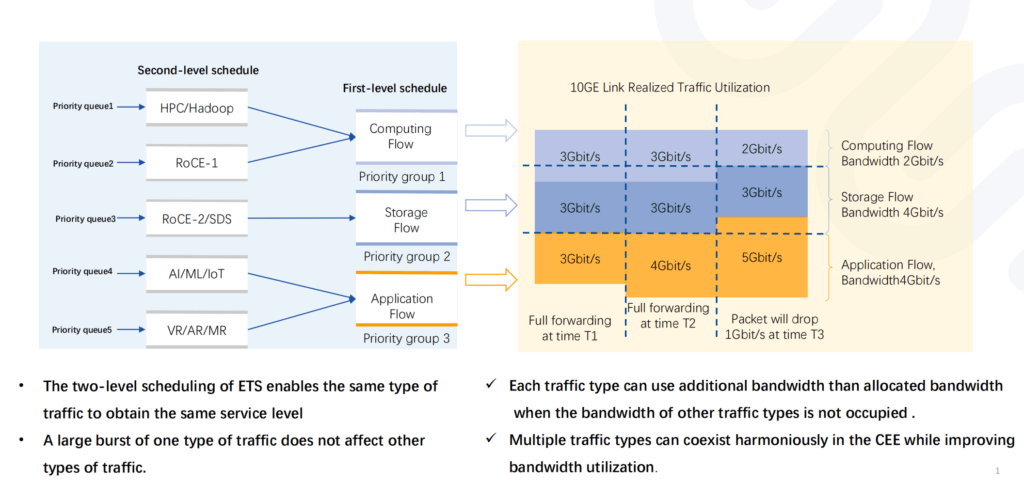
ETS provides the same level service for the same type RoCE flow and fully guarantees its bandwidth
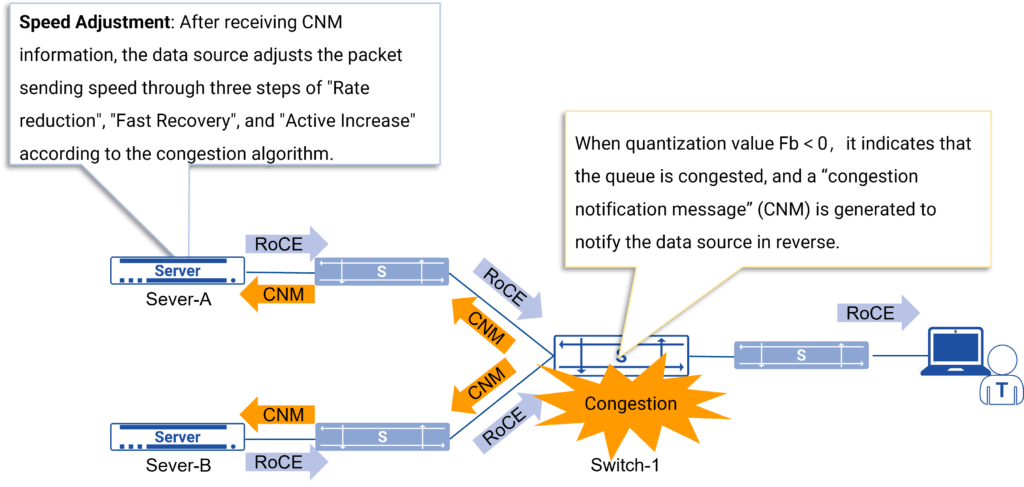
CN provides end-to-end congestion notification for RoCE to solve congestion at the source
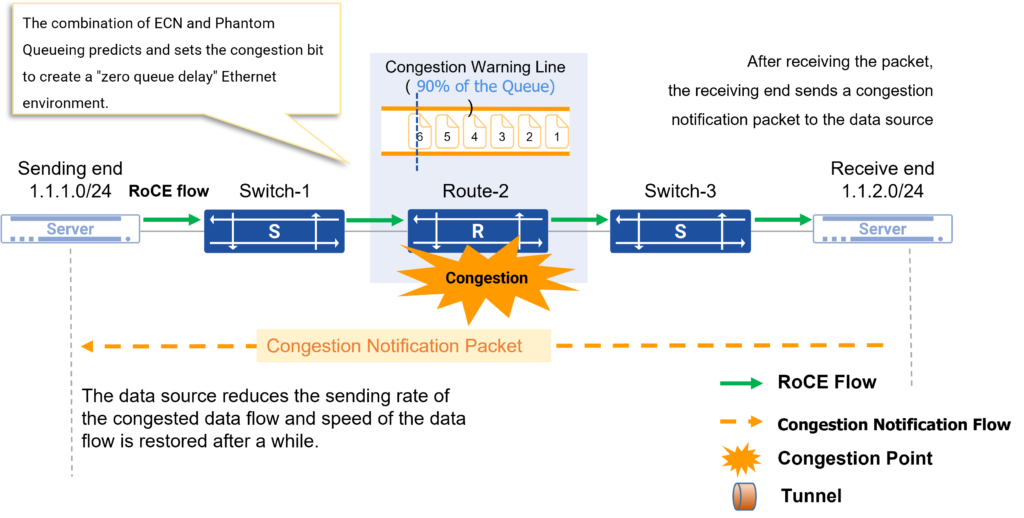
“ECN + Phantom Queueing” predict and avoid RoCE network congestion
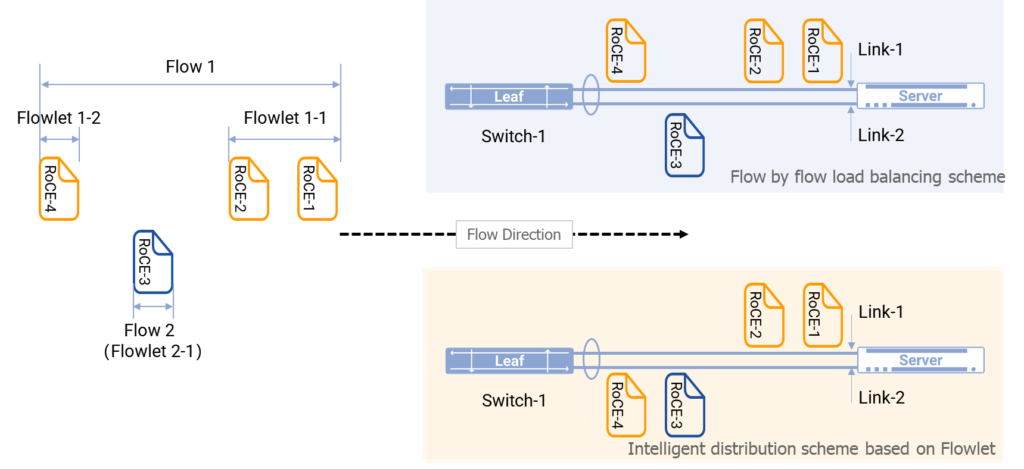
Hardware-assisted intelligent traffic distribution algorithm reduces the faults on RoCE traffic
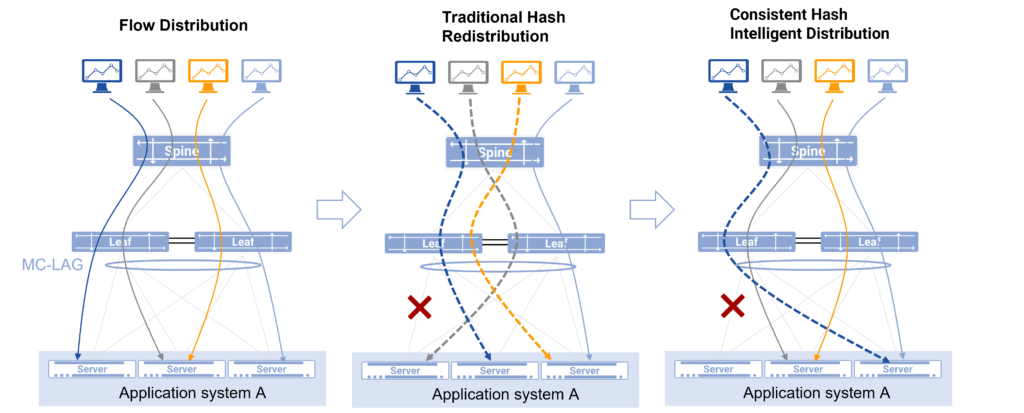
Intelligent Distribution of Several Flowlets of Elephant Flow in Asterfusion Cloud Network
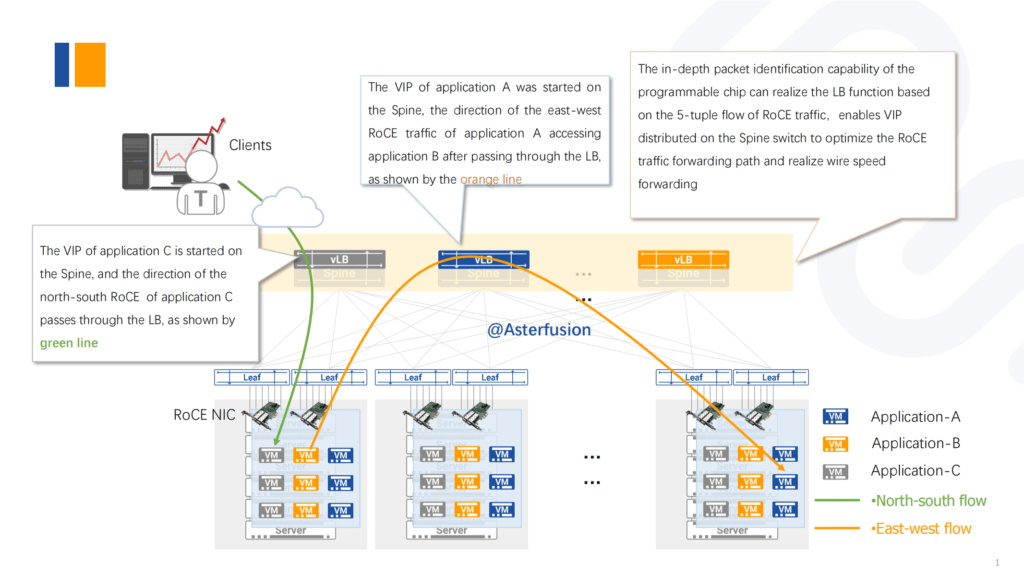
Enable Distributed vL4LB to optimize RoCE traffic forwarding paths
Everyone experiences network latency in all aspects of their daily business, it can be a serious threat to deadlines, expected results, and ultimate ROI for network operators and enterprises. This is where Asterfusion CX-N ultra-Low Latency Switch comes in. The Teralynx ASIC’s ultra-low Latency switching capability with powerful QoS features for RoCEv2, which can effectively increase bandwidth and reduces latency, jitter. Asterfusion CX-N switches enable to build highly efficient and cost-effective data center networks.
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latency_(engineering)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_delay
Bandwidth-delay product – Wikipedia
Related Products
-
 32-Port 400G QSFP-DD Low Latency AI/ML/Data Center Switch, Enterprise SONiC Ready,CX732Q-N
32-Port 400G QSFP-DD Low Latency AI/ML/Data Center Switch, Enterprise SONiC Ready,CX732Q-N -
 48-Port 25G Data Center Leaf (TOR) Switch with 8x100G Uplinks, SONiC Enterprise Ready, Marvell Falcon: CX308P-48Y-N
48-Port 25G Data Center Leaf (TOR) Switch with 8x100G Uplinks, SONiC Enterprise Ready, Marvell Falcon: CX308P-48Y-N -
 32-Port QSFP28 Low Latency Data Center Switch, Enterprise SONiC Ready, Marvell Teralynx: CX532P-N
32-Port QSFP28 Low Latency Data Center Switch, Enterprise SONiC Ready, Marvell Teralynx: CX532P-N