Table of Contents
Inband Network Telemetry (INT) is a network monitoring framework for collecting and reporting network status, which collected by a data forwarding plane without the intervention of control plane.
AI, big-data based Internet applications drive rapid upgrading of Internet data center products and technologies. On one hand, the access bandwidth was upgraded from the traditional 10Gbps to 25Gbps/100Gbps, the basic network is required to provide high forwarding capability to ensure the high availability of services.
On the other hand, with the widespread application of Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) lossless Ethernet technology, realize microsecond-level delay from computing node to storage node, which greatly optimizes forwarding performance of end-to-end service. And that also means higher challenges to network operation and maintenance–So, how to achieve more sophisticated traffic visualization and controllability in a large, complex HPC (high performance computing) network; how can we achieve end-to-end seconds- level failure positioning for service ?
This article introduces the In-band network telemetry technology , which provides new ideas for realizing the whole network traffic visualization.
What is INT(In-band Network Telemetry)
Inband Network Telemetry (INT) is a network monitoring framework for collecting and reporting network status, which collected by a data forwarding plane without the intervention of control plane .In an INT-defined framework, the messages can carry INT instructions which can be interpreted by the intermediate forwarding device and filled in with the expected data, and then continue to be forwarded until the destination. INT could be able to observe flow pattern changes caused by microbursts, packet transmission delays, delays per node, and new ports in the flow path.
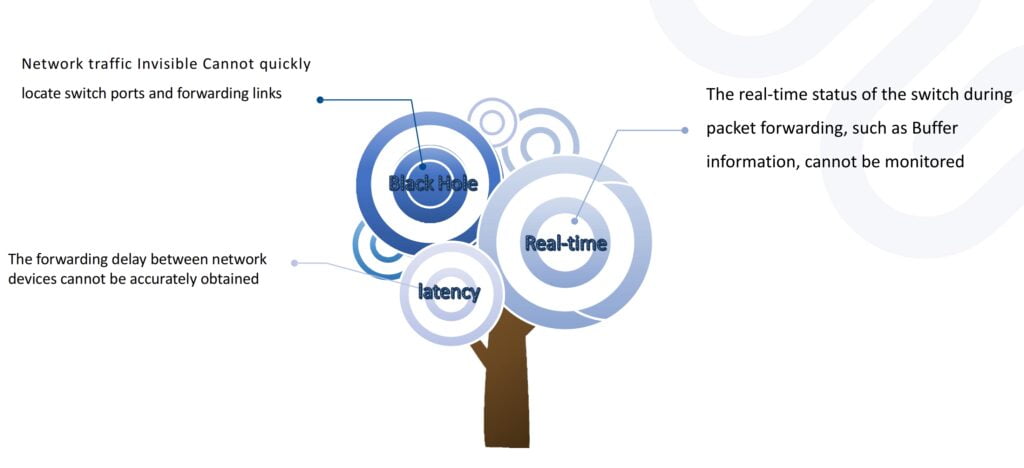
Why INT(In-band Network Telemetry)is Important?
Challenges encountered in traditional network operation and maintenance
While the network interface rate develops from 1Gbps to 25Gbps100 Gbps, the increase of the cache capacity of the switch chip has not kept up, and the available cache time decreases instead.
Instantaneous many-to-one causes packet congestion on the egress. When the egress cache is used up, packets are discarded based on the tail discard mechanism . The application monitors packet loss and initiates TCP retransmission, causing the data end-to-end delay to worsen, seriously affecting the service experience.
In traditional networks, the SNMP protocol, which is initiated by external applications to request network status information. It can only passively wait for the timeout or the peer feedback to be received ,which feels like the delivery cannot be tracked.
However, for service failures caused by network packet loss, the network monitoring system is required to quickly locate which switch and port has lost packets due to insufficient cache. Meanwhile, when the critical application end-to-end delay exceeds expectations, it’s also necessary to locate the forwarding delay of each node on the traffic forwarding path.
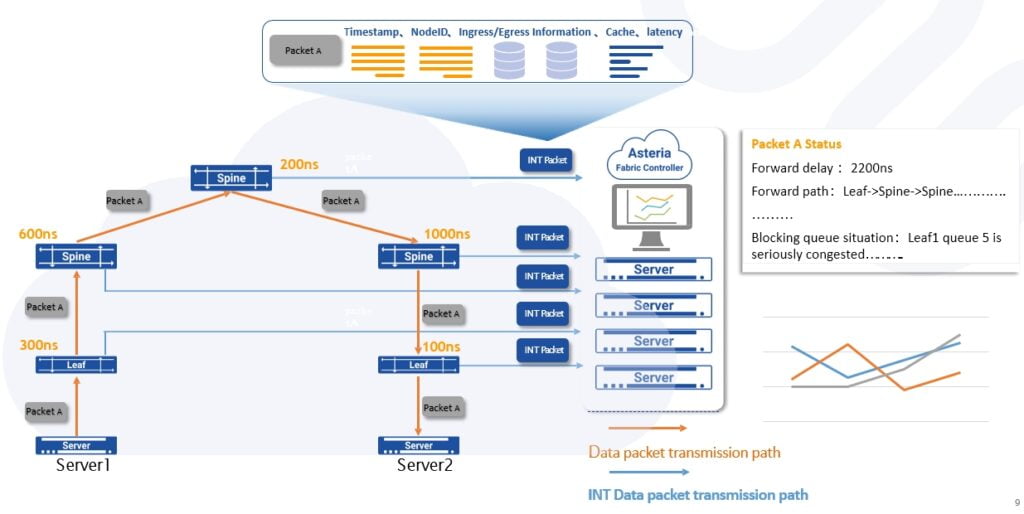
In-band Network Telemetry : A Strong Network Monitoring Framework
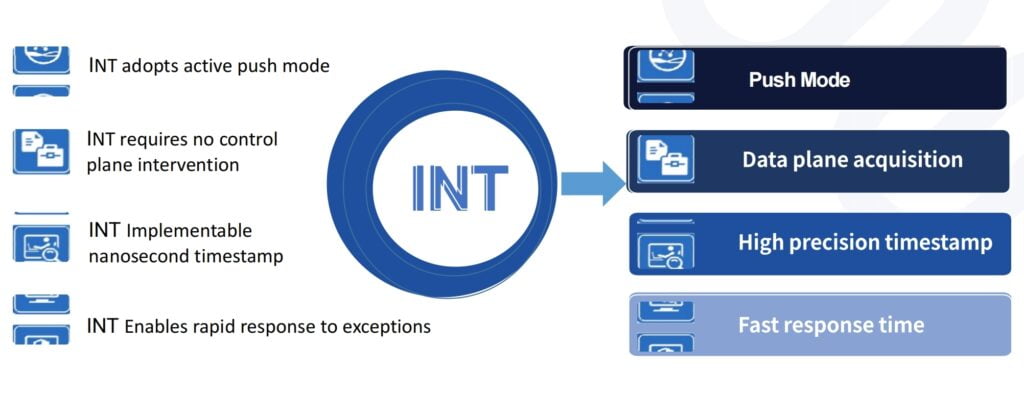
In order to solve the problem of “invisibility” that cannot be solved by traditional network , the industry has widely introduced INT(Inband Network Telemetry). Compared to SNMP, It realizes the ability of network equipment to actively push status information, has stronger timeliness, and solves the problem of invisible forwarding path and forwarding delay.
INT technology has been developed for near 8 years, which involves many addition and deletion of technical details. It is currently dominated by the P4.org applications working group. Its main development process is as follows:
- 2015-09-28 Initial release
- 2017-12-11 v0.5 spec released
- 2018-04-20 v1.0 spec released
- 2020-02-14 v2.0 spec released
For more about P4 knowledge https://switchicea.com/blogs/what-you-should-know-about-p4-programming-language-p4-switch/
How Does Telemetry Realize Network Traffic Visualization
Generally speaking, an INT domain contains three main function nodes, INT Source, INT Sink and INT Transit Hop.
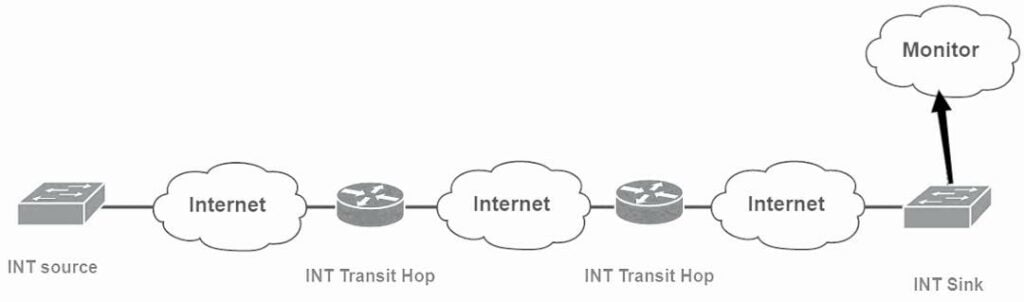
For the telemetry operater, the traffic that needs to be telemetry will add an INT header to the source node, which contains an instruction set (INT Instruction) indicating the collected information, thus becoming an INT message. When the INT Transit Hop node is installed, the collected information (INT Metadata) will be inserted into the INT message according to the instruction set, and finally all the INT information will be popped up on the INT Sink node and sent to the monitoring device.
For users, the INT processing of traffic is completely transparent and users cannot and do not need to perceive the process.
Let us review the process in detail:
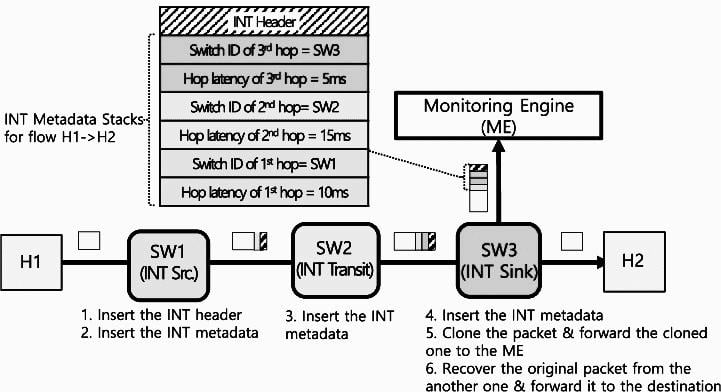
- Host H1 sends a data packet to H2
- SW1 inserts the INT header into the packet, the header source is SW1 and the sink is SW3
- SW1’s instruction is to collect SW ID and forwarding delay
- SW1 inserts its own ID and forwarding delay from ingress to exgress
- the middle switch SW2, SW3 repeat this process
- SW3 is the INT sink, which is responsible for summarizing the INT collection information and sending it to the report server.
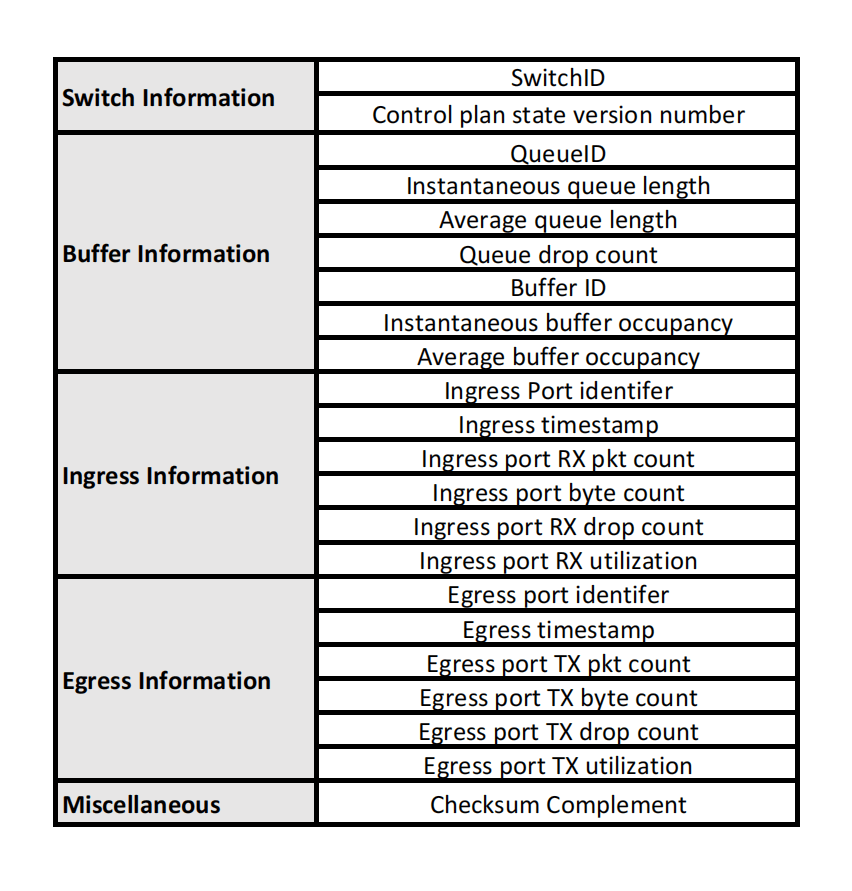
Network Monitoring Information that INT can Collect
The information defined by the INT protocol is mainly divided into the following categories:
Advantages of INT : Realize Network Traffic Visualization in Data Center
Aserfusion Data Center Leaf Spine Switches Support INT Function
The Asterfusion CX-N low latency switches based on Marvell Teralynx and X-T based P4 programmable switches based on Intel Tofino support INT(In-band Network Telemetry) which provides accurate and comprehensive real- time network telemetry information including port interfaces, packet latency, packet queue lengths, etc. Cloud data center network administrators can leverage INT information to optimize their business applications and network operations, helping to build efficient, intelligent and highly resilient data center networks.


Asterfusion Cloud Switches enable Data Center Realize Network Traffic Visualization
Quickly locate network faults – get clear packet forwarding paths
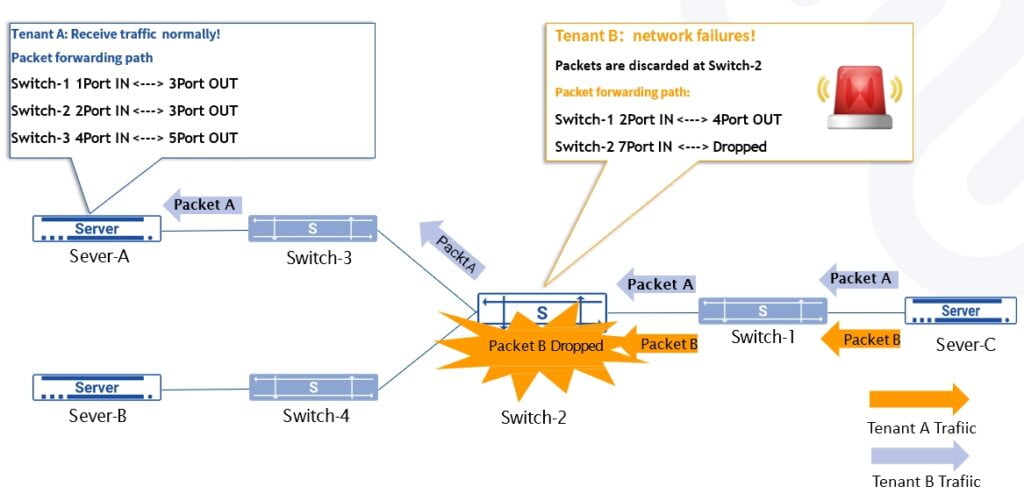
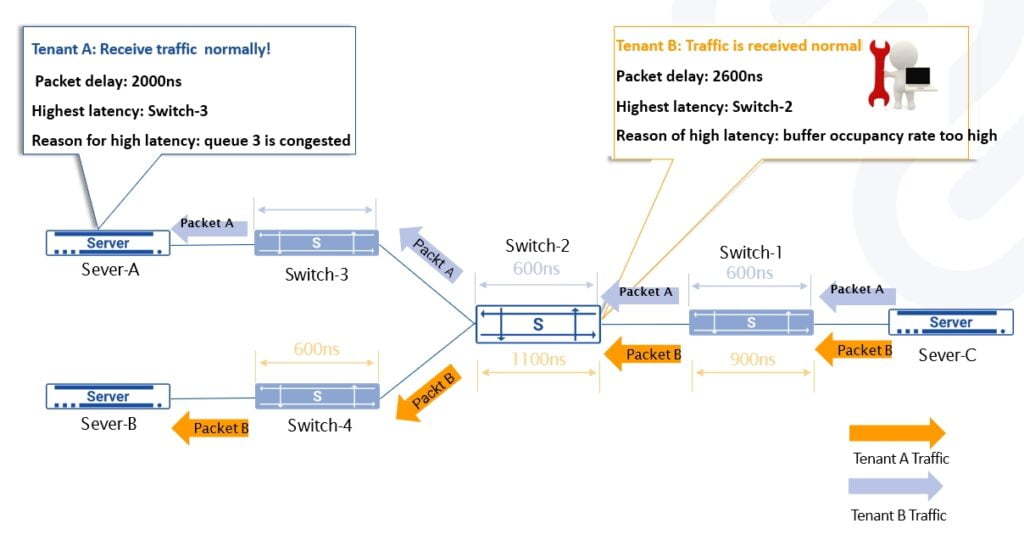
Improve packet forwarding performance – Get accurate packet forwarding delay
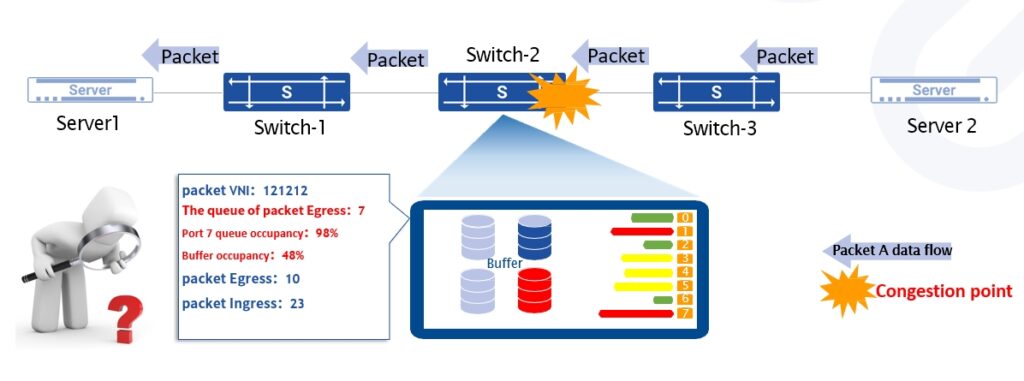
Quickly identify network bottlenecks – Get real-time packet forwarding status
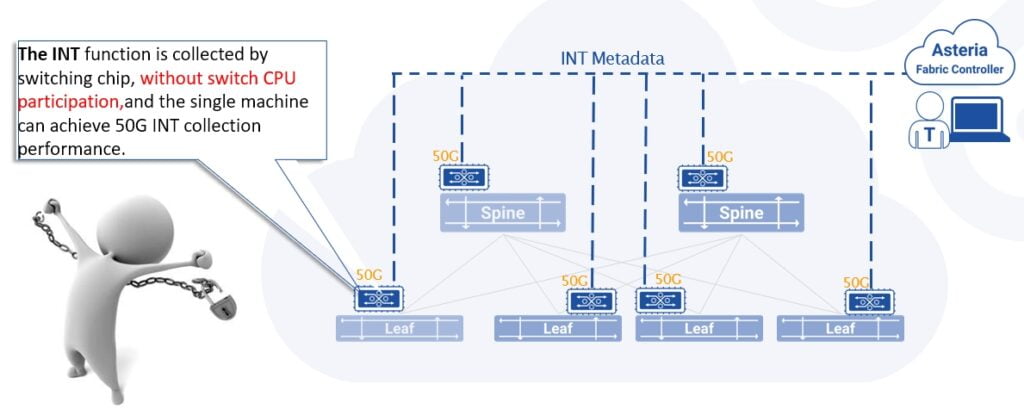
Ultra High Performance Telemetry – Fully Automated Data Plane Processing
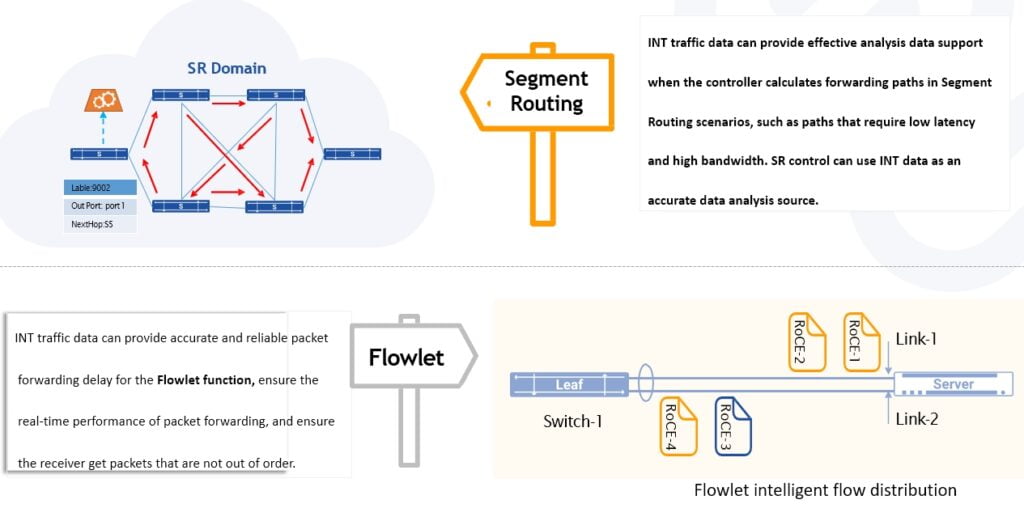
Provide basic analysis telemetry data for many applications
Configuration automation – AFC Controller automatically delivers configuration
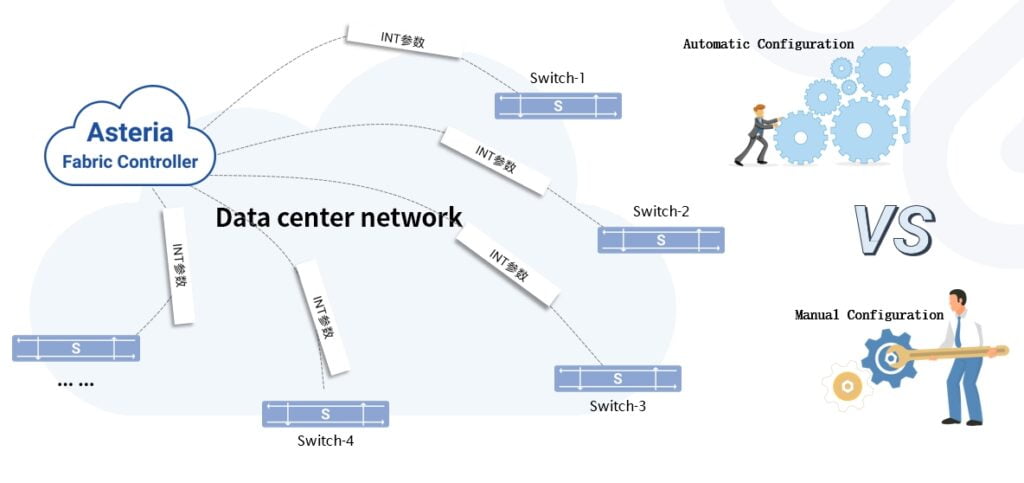
For the next generation of data center networks for HPC services, INT-based technology enables end-to-end network traffic visualization ,which breaks the “network black box” and provide overall solutions and necessary technical support for refined network operation and maintenance.
Reference:
https://github.com/p4lang/p4-applications/tree/master/docs
https://p4.org/assets/INT-current-spec.pdf
https://www.sdnlab.com/23822.html






