A Comparative Analysis of InfiniBand and RoCE for AI Data Centers
written by Asterfuison
Table of Contents
In the increasingly fierce competition between InfiniBand and Ethernet for market dominance in AI backend networks, manufacturers are battling to provide a high-performance network infrastructure. This is crucial to support the operation of AIGC. To meet the demands of AI cluster computing, the industry has put forward two main network solutions: InfiniBand and RDMA. In this comparison, we will delve into these two technologies.

Understanding of InfiniBand
What is InfiniBand?
InfiniBand (abbreviated as IB), is a communication standard for high-performance computing that offers remarkable throughput and minimal latency for computer-to-computer data interconnections. It is used both as a direct or switched interconnect between servers and storage systems, as well as an interconnect between storage systems. With the exponential growth of artificial intelligence, InfiniBand has become the preferred network interconnect technology for GPU servers.
InfiniBand’s network architecture
InfiniBand is a communications link for data flow between processors and I/O devices, supporting up to 64,000 addressable devices. InfiniBand Architecture (IBA) is an industry-standard specification that defines a point-to-point switching input/output framework for interconnecting servers, communications infrastructure, storage devices, and embedded systems.
InfiniBand is ubiquitous, low-latency, high-bandwidth, and low-management cost, and is ideally suited for connecting multiple data streams (clustering, communications, storage, management) in a single connection with thousands of interconnected nodes. The smallest complete IBA unit is a subnet, and multiple subnets are connected through routers to form a large IBA network.
An InfiniBand system consists of channel adapters, switches, routers, cables, and connectors. the CAs are categorized as host channel adapters (HCAs) and target channel adapters (TCAs). IBA switches are similar in principle to other standard network switches but must meet the high performance and low cost requirements of InfiniBand. The HCA is the device point at which IB end nodes, such as servers or storage devices, connect to the IB network. the TCA is a special form of channel adapter used primarily in embedded environments, such as storage devices.
The HCA is the device point where IB end nodes (such as servers or storage devices) connect to the IB network. TCA is a special form of channel adapter used primarily in embedded environments such as storage devices.
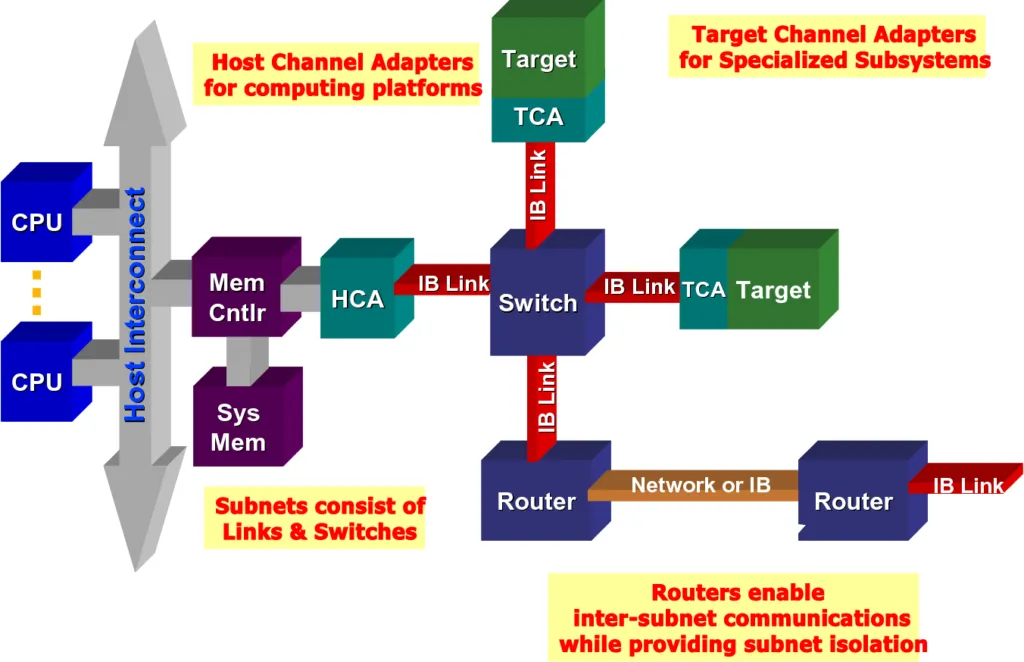
InfiniBand has the following advantages
- Low Latency: InfiniBand networks are known for their extremely low latency. RDMA zero-copy networks reduce operating system overhead, allowing data to move quickly through the network.
- High Bandwidth: InfiniBand networks offer high bandwidth data transfer capabilities. It usually supports tens of Gb/s or even higher bandwidth, high bandwidth makes it possible to exchange data between nodes at high speed.
- High throughput: Due to the characteristics of low latency and high bandwidth, IB networks are able to realize high throughput data transmission. It supports parallel transmission of large-scale data streams, while reducing intermediate processing and copy operations
- Scalability: It supports multi-level topologies, such as global interconnection networks, tree structure and flat structure, which can be flexibly configured and expanded according to application requirements and scale.
Which manufacturers on the market support InfiniBand?
- Mellanox: Mellanox is basically the only manufacturer of IB switches in the world. NVIDIA successfully acquired it in 2020 and now also offers NVIDIA Quantum InfiniBand switches.
- HP, DELL, etc.: These companies are mainly OEMs, which means they do not directly produce IB switches, but purchase or obtain authorization from manufacturers such as Mellanox, and then conduct re-sells.
InfiniBand‘s shortcomings and limitations:
Since InfiniBand (IB) boasts numerous ultimate advantages, it is intriguing to wonder why the industry is increasingly expressing hopes for Ethernet to become the preferred technology for artificial intelligence workloads amidst the explosive development of artificial intelligence. As time goes by, it has been revealed that the industry has also discovered several fatal shortcomings of InfiniBand:
- Very High Costs: The primary drawback of InfiniBand is its exorbitant price tag when compared to Ethernet. Constructing a dedicated network using InfiniBand requires a designated IB network card and switch, which generally costs five to ten times more than ordinary network equipment. Consequently, InfiniBand is only seriously considered for implementation in high-end industries such as finance and futures trading.
- Elevated O&M Expenses: InfiniBand, being a dedicated network technology, cannot leverage the user’s existing IP network infrastructure and accumulated knowledge in terms of operation and maintenance. Enterprises opting for InfiniBand must hire specialized personnel to handle the specific operation and maintenance requirements. However, due to the limited market space occupied by InfiniBand (less than 1% of Ethernet), there is a severe shortage of experienced operation and maintenance personnel in the industry. Network failures may go unrepaired for extended periods of time, leading to exorbitant operational expenses (OPEX).
- Vendor lock in: The presence of vendor lock-in is a major drawback of InfiniBand switches. These switches are manufactured by specific vendors and use proprietary protocols, making it difficult for them to communicate with other network devices that use IP Ethernet. This closed architecture also poses a risk to businesses that require scalable expansion in the future, as being tied to a single vendor can lead to uncontrollable risks.
- Long lead time: The long lead time of InfiniBand switches is another concern. Their arrival is unpredictable, which increases project risk and hampers business expansion.
- Slow upgrade: The upgrade process of the network depends on individual vendors’ product releases, preventing unified upgrades across the industry. This slowness in upgrades can hinder the overall progress of the network.
But What is better than InfiniBand?
Compared to InfiniBand, RoCE provides greater versatility and better price/performance ratio. It not only allows the construction of high-performance RDMA networks but is also compatible with traditional Ethernet networks.
What is ROCE?
RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) is a cutting-edge network protocol that facilitates direct transfer of memory data between computers without the involvement of the CPU or operating system. This not only frees up memory bandwidth and CPU cycles, but also enhances system performance, enabling faster communication between nodes with lower latency and increased throughput. RDMA technology is currently extensively used in various high-performance scenarios such as supercomputing, AI training, and storage.
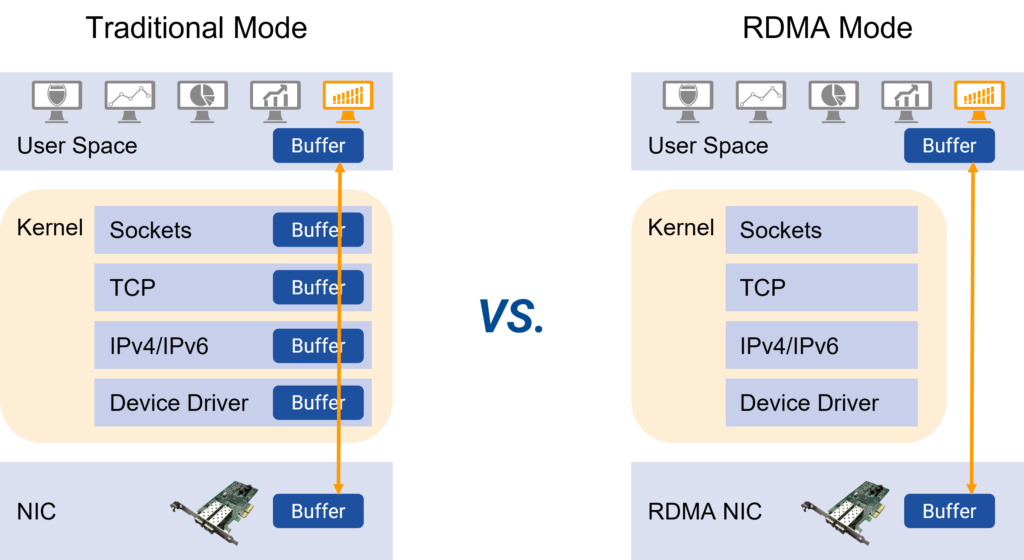
RDMA technology implementation routes include the following three types:
- InfiniBand: the earliest RDMA technology implemented;
- RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet): RDMA technology based on ordinary Ethernet;
- iWARP: Internet Wide Area RDMA Protocol, RDMA technology based on TCP/IP protocol stack.
RoCEv1 is implemented on the Ethernet link layer, using features like PFC and other flow control technologies to ensure reliable transmission at the physical layer. On the other hand, RoCEv2 utilizes the Ethernet TCP/IP protocol in the UDP layer, addressing scalability concerns and overcoming certain limitations of InfiniBand technology. This enables broader adoption of RDMA technology in data centers, cloud computing, and other domains. Furthermore, the development of RoCEv2 can drive standardization and popularization of RDMA technology, making it more accessible and user-friendly.
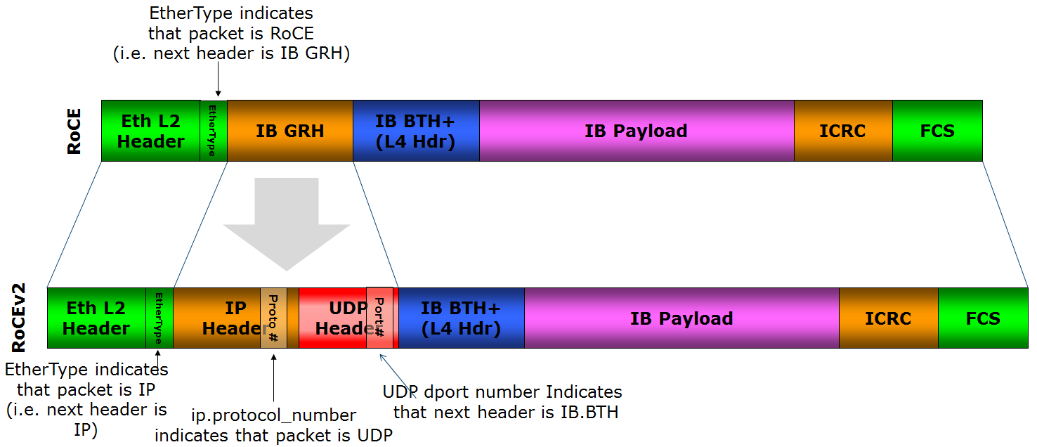
For more about ROCE /iWARP/InfiniBand,PLEASE read:
Advantages of RoCEv2
- Similar Performance: There is minimal difference in end-to-end latency between ROCE and IB in specific scenarios (such as distributed storage) while considering the latency of network cards and software applications
- Lower Cost:RoCE v2 presents a lower lost compared to InfiniBand, making it a more budget-friendly choice for organizations seeking to implement high-performance networking solutions while efficiently managing expenses. This enhanced cost-effectiveness enhances its engagement.
- Compatibility with Ethernet Networks: Another key benefits of RoCE v2 is its compatibility with Ethernet networks. It operates seamlessly on routed Ethernet networks, which are commonly found in large data centers. RoCE v2 is carried on Ethernet, allowing the use of optical fibers and optical modules of traditional Ethernet. This compatibility with existing infrastructure simplifies integration and minimizes the need for extensive network overhauls, resulting in improved engagement.
Which manufacturers on the market support ROCEv2 ready data center switch?
Cisco, Arista, NVIDIA’s ConnectX series, Juniper,Aruba CX Switches, Dell EMC OS10, Asterfusion CX-N low latency series
Comparison of InfiniBand and RoCE v2
| InfiniBand | RoCE | |
| Port-to-Port Delay | About 130 ns | About 400 ns |
| Flow Control | Utilizes a credit-based signaling mechanism to avoid buffer overflow and packet loss, ensuring lossless HCA-to-HCA communication. | Relies on lossless Ethernet, typically configured via Ethernet flow control or priority flow control (PFC) for reaching performance characteristics similar to InfiniBand |
| Forwarding Mode | Forwarding based on Local ID | IP-based Forwarding |
| Scalability | High. A single subnet of Infiniband can support tens of thousands of nodes. It also provides a relatively simple and scalable architecture to create virtually unlimited cluster sizes with Infiniband routers. | High. RoCEv2 is based on UDP and has good scalability across network segments, so it is a solution adopted on a large scale. RoCE supports dynamic creation and adjustment of network topology, making it adaptable to the needs of data centers of different sizes. |
| Reliability | Implemented through InfiniBand proprietary protocol combined with adaptive routing | IP-based ECMP mechanism is realized. In addition, RoCE supports error correction and retransmission mechanisms, further improving the reliability of data transmission. |
| Cost | Very expensive: servers require dedicated IB NICs, dedicated IB switches to build a dedicated network, generally five to ten times the cost of ordinary network equipment, and are only considered for use in high profile environments such as finance and futures trading | Lower cost Excellent price/performance ratio Some of the white box manufacturers’ ROCE v2 -ready data center switches are about half or even a third of the price of an IB switch |
Asterfusion AI Data Center Networking Solution
The NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD™ with NVIDIA DGX™ H100 systems is the cutting-edge data center architecture for AI. Asterfusion provides another approach of RoCEv2 enabled 100G-800G Ethernet switches to build a DGX H100 based superPOD instead of InfiniBand switches, including compute fabric, storage fabric, in-band and out-of-band management network.
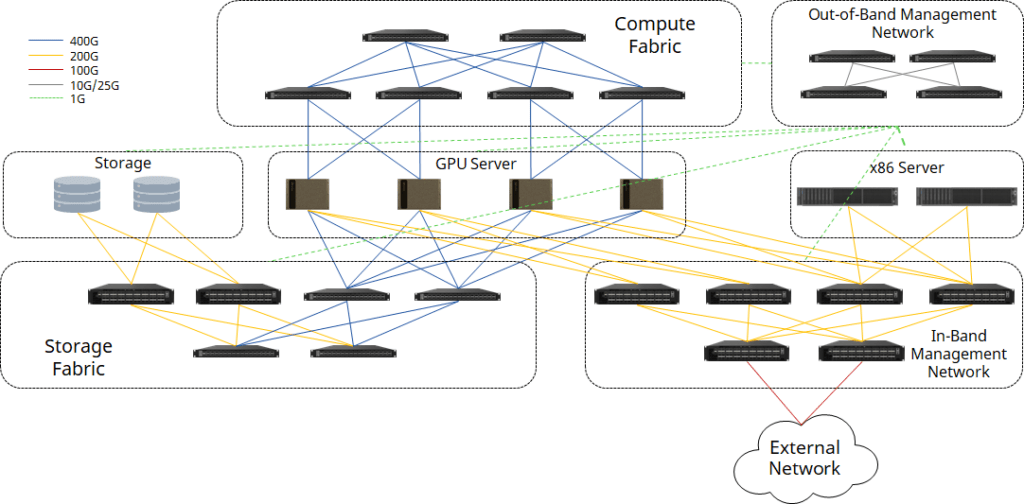
Compute Fabric
For a research project or PoC, starting with a small-scale cluster is a good choice. Less than 4 nodes DGX H100 can be connected with one single 32x400G switch, using QSFP-DD transceivers on switch ports and OSFP transceivers on ConnectX-7 NIC of each GPU server, connecting by MPO-APC cables.

When the number of GPU servers increases to 8, a 2+4 CLOS fabric can be applied. Each leaf switch connects 2 of 8 ports of each GPU server, to archieve a rail-optimized connectivity to increase the efficiency of GPU resources. Spine and leaf switches can be connected through QSFP-DD transceivers with fiber, or QSFP-DD AOC/DAC/AEC cables.

Single CX864E-N (51.2Tbps Marvell Teralynx 10 based 64x800G switch, coming in 2024Q3) can hold even up to 16 GPU servers:

A scalable compute fabric is built upon modular blocks, which provides a rapid deployment of multiple scales. Each block contains a group of GPU servers and 400G switches (16 x DGX H100 systems with 8 x CX732Q-N in this example). The block is designed as rail-aligned and non-oversubscribed, to ensure the performance of the compute fabric.

A typical 64-node compute fabric design is to use Leaf-Spine architecture to hold 4 blocks:

To scale the compute fabric, higher throughput switches can be used to replace the Spine. CX864E-N can be placed here to expand the network to maximum 16 blocks of 256 nodes:

For more about Asterfusion AI network solution : please visit https://cloudswit.ch/solution/rocev2-ai-solution-with-dgx-superpod/
NVIDIA InfiniBand Vs Asterfusion RoCEv2 switch’s Onsite Test Data
Please visit: https://cloudswit.ch/blogs/sonic-switches-rocev2-test-in-aigc-hpc-storage/
It is noteworthy that Asterfusion RoCE-based switches are priced at less than half the cost of IB switches.
How to choose from InfiniBand and RoCE for AI data center?
While InfiniBand is expected to maintain its leadership position, Ethernet is projected to make significant gains, such as 20 revenue share points by 2027, according to the latest AI Networks for AI Workloads report from Dell’Oro Group.
Organizations choosing between RoCE and Infiniband should consider their unique requirements and costs. If they prefer the highest performance network connectivity, Infiniband is better. And for those looking for optimal performance, ease of management and limited cost, they should choose RoCE for their data center.
RoCE Configuration on Asterfusion Enterprise SONiC Distribution Switch
RoCE Configuration on Asterfusion Enterprise SONiC Distribution Switch
For more:please cotact: bd@cloudswit.ch
Reference:






